Properties and Applications of Composite Material
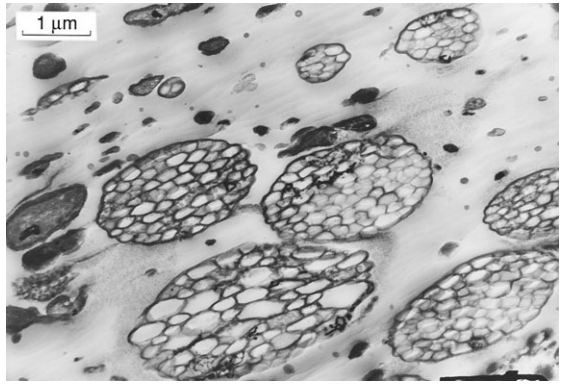
A composite material is made by combining two or more materials that are mutually insoluble by mixing or bonding them in such a way that each maintains its integrity. Some composites, plastics modified by adding rubber particles, plastics reinforced by chopped glass fibers, cemented carbides, and concrete. These and many other composite materials consist of […]
Properties and Applications of Composite Material Read More »