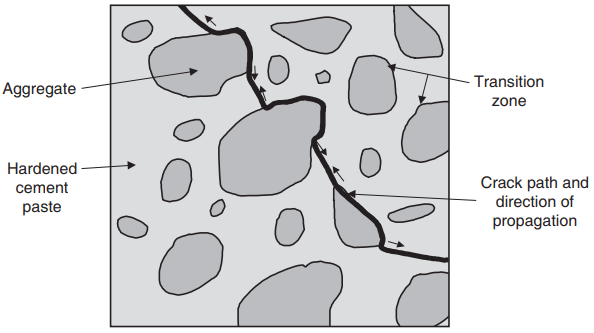
Early Age Properties of Concrete
Successful placing of concrete is not enough. It is necessary to ensure that it comes through the first few days of its life without mishap, so that it goes on to have the required mature properties. Immediately after placing, before the cement’s initial set the concrete is still in a plastic and at least semi-fluid […]